문제
N(2 ≤ N ≤ 40,000)개의 정점으로 이루어진 트리가 주어지고 M(1 ≤ M ≤ 10,000)개의 두 노드 쌍을 입력받을 때 두 노드 사이의 거리를 출력하라.
풀이
백준 1761 (정점들의 거리) - LCA 풀이
문제 N(2 ≤ N ≤ 40,000)개의 정점으로 이루어진 트리가 주어지고 M(1 ≤ M ≤ 10,000)개의 두 노드 쌍을 입력받을 때 두 노드 사이의 거리를 출력하라. 풀이 선형 시간의 LCA 알고리즘을 사용하였다. 해
conpulake.tistory.com
앞서 선형방식으로 간단하게 풀었지만 SparseTable을 이용해서 풀면 시간복잡도가 훨씬 줄어든다.
백준 11438 ( LCA 2) - DP 풀이
문제 N(2 ≤ N ≤ 100,000)개의 정점으로 이루어진 트리가 주어진다. 트리의 각 정점은 1번부터 N번까지 번호가 매겨져 있으며, 루트는 1번이다. 두 노드의 쌍 M(1 ≤ M ≤ 100,000)개가 주어졌을 때, 두
conpulake.tistory.com
여기서 SparseTable 을 이용해 LCA 를 구하는 법을 풀이했다 이 풀이를 이용하여 문제를 풀었다.
새롭게 선언한 배열은
dist[] : 정점에서 가장 작은 조상까지의 거리를 저장하는 배열
이렇게 있다.
문제에서 입력하는 정점을 그래프로 표현을 하면
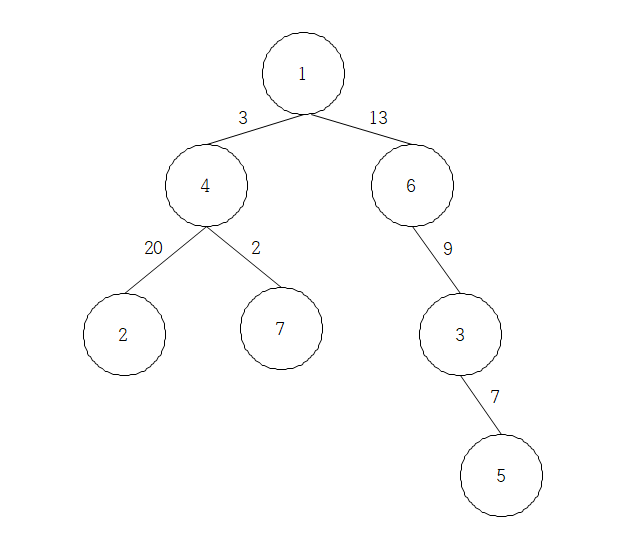
위 그림과 같은 그래프가 나온다.
여기서 DFS 함수를 이용해서 dist 배열을 저장을 하고 나면
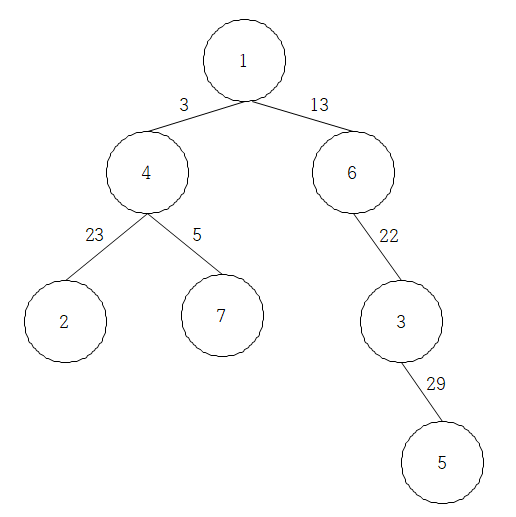
이런 식으로 제일 작은 조상까지의 거리를 모두 더한값을 가지게 된다.
따라서 a, b 정점의 거리는 dist[a] + dist[b] - 2 * dist[LCA(a,b)] 가 된다.
예를들어 2 와 7의 사이 거리는
dist[2] = 23
dist[7] = 5 이다. 이는 공통조상 4에서 1까지의 거리까지를 더해진 값이므로
dist[2] = 23 - dist[4]
dist[7] = 5 - dist[4] 이 된다.
따라서 2, 7 의 사이 거리는 dist[2] + dist[7] - 2 * dist[4] 가 된다. 이를 이용해 문제를 풀면 된다.
<전체코드>
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static class node{
public int num, dist;
public node(int num, int dist) {
this.num = num;
this.dist = dist;
}
}
static StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
static int[] depth;
static int[][] parents;
static int[] dist;
static List<node>[] tree;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int n = Integer.parseInt(bufferedReader.readLine());
tree = new List[n + 1];
for(int i = 0 ; i <= n ; i++) {
tree[i] = new LinkedList<node>();
}
for(int i = 0 ; i < n - 1; i++) {
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(bufferedReader.readLine());
int a = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int b = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int dist = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
tree[a].add(new node(b, dist));
tree[b].add(new node(a, dist));
}
int tmp = 1;
int K = 0;
while(tmp <= n) {
tmp <<= 1;
K++;
}
depth = new int[n + 1];
parents = new int[n + 1][K];
dist = new int[n + 1];
DFS(1, 1);
DP_Algorithm(K, n);
int m = Integer.parseInt(bufferedReader.readLine());
for(int i = 0 ; i < m ; i++) {
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(bufferedReader.readLine());
int a = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int b = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int lca = LCA(a, b, K);
sb.append(dist[a] + dist[b] - 2 * dist[lca] + "\n");
}
System.out.println(sb);
}
public static void DFS(int node, int cnt) {
depth[node] = cnt;
for(node next : tree[node]) {
if(depth[next.num] == 0) {
parents[next.num][0] = node;
dist[next.num] = dist[node] + next.dist;
DFS(next.num, cnt + 1);
}
}
}
public static void DP_Algorithm(int k, int n) {
for(int i = 1; i < k ; i++) {
for(int j = 1; j <= n ; j++) {
parents[j][i] = parents[parents[j][i - 1]][i - 1];
}
}
}
public static int LCA(int a, int b, int k) {
if(depth[a] < depth[b]) {
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
for(int i = k - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) {
if(Math.pow(2, i) <= depth[a] - depth[b]) {
a = parents[a][i];
}
}
if(a == b)
return a;
for(int i = k - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) {
if(parents[a][i] != parents[b][i]) {
a = parents[a][i];
b = parents[b][i];
}
}
return parents[a][0];
}
}
★

위 풀이를 통해 밑에가 SparseTable을 이용하여 풀이를 한경우고
위에가 선형풀이바식으로 거리를 그때그때 다 더해서 구한 방식이다.
시간이 훨씬 적게 걸리는것을 볼 수있다.
'자료구조 공부 > Tree 구조 알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [백준] 15681 트리와 쿼리 <Java> - 트리에서 DP (0) | 2022.01.07 |
|---|---|
| [백준] 2263 트리의 순회(분할정복) (0) | 2021.11.05 |
| [프로그래머스] 길 찾기 게임 (0) | 2021.05.30 |
| 백준 3176 (도로 네트워크) - LCA 풀이(Sparse Table 사용) (0) | 2021.03.30 |
| 백준 11438 (LCA 2) - 최소공통조상(HLD 풀이) (0) | 2021.03.24 |